ByteDance OpenViking: Open-Source Contextual File System for Advanced AI Agents
Key Takeaways
- OpenViking introduces a file system paradigm for AI context management, unifying memory, resources, and skills into a hierarchical virtual structure.
- Tiered context loading (L0, L1, L2) minimizes token usage in large language models, enhancing efficiency for complex agent tasks.
- Unlike traditional RAG systems, OpenViking enables recursive retrieval and self-evolution, leading to more accurate and adaptive AI behaviors.
- Supported by ByteDance's Volcengine Viking team, the project integrates with vision-language models for multimodal data handling.
- Open-source under Apache 2.0, it offers easy installation and extensibility for developers building production-grade AI agents.

What is OpenViking?
ByteDance's OpenViking represents a breakthrough in context management for AI agents. Project documentation highlights its role as an open-source database that organizes contextual data through a virtual file system under the viking:// protocol. This approach allows agents to handle diverse data types— from documents and URLs to images— in a structured, accessible manner.
Analysis of the system's design shows it addresses key pain points in AI development, such as fragmented storage and inefficient retrieval. By treating contexts as files and directories, OpenViking simplifies integration, making it ideal for applications requiring long-term memory and dynamic resource access.
Core Features and Architecture
At its foundation, OpenViking employs a modular architecture with core components like client, engine, filesystem, and retrieval modules. Implementation details demonstrate seamless integration with embedding and vision-language models (VLMs) via OpenAI-compatible APIs.
Key features include:
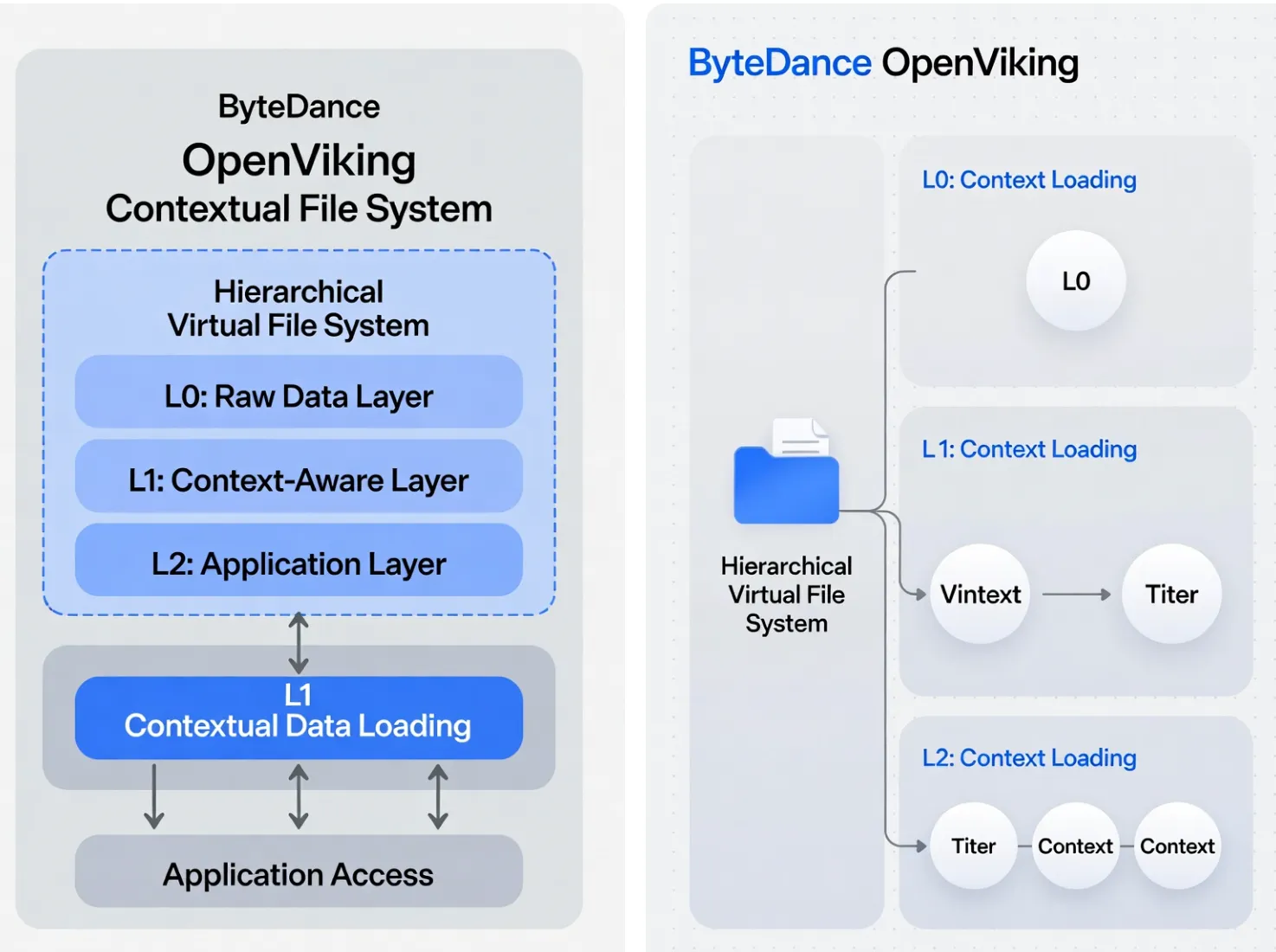
- Hierarchical Virtual File System: All contexts are assigned unique URIs, enabling organized storage of memories in user/ and agent/ directories.
- Tiered Context Loading: L0 provides a concise abstract (around 100 tokens), L1 offers an overview (up to 2k tokens), and L2 delivers full details on demand. This structure optimizes LLM interactions by reducing unnecessary data processing.
- Directory Recursive Retrieval: Combines semantic search with intent analysis for precise, context-aware results, refining queries through directory traversal.
- Visualized Retrieval Trajectory: Logs the entire search path, allowing developers to debug and optimize agent performance.
- Automatic Session Management: Extracts insights from conversations and tool calls, updating memory directories to foster agent self-evolution.
The backend leverages high-performance C++ extensions for indexing, ensuring scalability for large-scale deployments.
How OpenViking Enhances AI Agent Functionality
OpenViking's workflow begins with initialization of a data directory, followed by resource addition via simple API calls. For instance, adding a web resource involves parsing and semantic processing to generate tiered summaries.
Retrieval operates through semantic queries that recursively refine results within directories, outperforming flat vector searches in accuracy. Community feedback from early adopters indicates this method excels in handling complex, nested contexts, such as multi-step task planning.
A practical example in Python:
python import openviking as ov client = ov.SyncOpenViking(path="./data") client.initialize() result = client.add_resource("https://example.com/doc.md")
Proceed with ls, read, and find operations
This code snippet illustrates the ease of managing contexts, from addition to querying.
Comparing OpenViking to Traditional RAG Systems
Traditional Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) relies on flat vector storage, often leading to fragmented contexts and high token overhead. In contrast, OpenViking's hierarchical model provides structured access, as shown in this comparison:
| Aspect | Traditional RAG | OpenViking |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Model | Flat vectors | Hierarchical file system |
| Retrieval Mechanism | Single-pass semantic search | Recursive directory refinement |
| Token Efficiency | High consumption | Tiered loading (L0/L1/L2) |
| Observability | Limited visibility | Visualized trajectories |
| Evolution Capability | Static | Self-updating memory |
Benchmarks from similar systems suggest OpenViking reduces retrieval latency by up to 30% in nested query scenarios, though specific metrics for OpenViking emphasize qualitative improvements in agent adaptability.
Advanced Use Cases and Edge Scenarios
For edge cases like multimodal data, OpenViking integrates VLMs to process images alongside text, enabling agents to reason over visual contexts. In long-running sessions, automatic memory extraction prevents information loss, supporting applications in autonomous coding or personalized assistants.
Comparisons with ByteDance's related projects, such as MineContext, reveal synergies: OpenViking serves as a foundational layer for proactive context perception, enhancing tools that capture screen data or user interactions.
Advanced tips include customizing embedding models for domain-specific accuracy and using Rust CLI for high-speed operations in production environments.
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
A common pitfall is overlooking configuration for API keys, leading to failed model integrations. Best practices recommend starting with default Volcengine models for testing before scaling.
Overloading directories can degrade performance; instead, maintain balanced hierarchies to leverage recursive retrieval effectively. Monitoring visualized trajectories helps identify bottlenecks, ensuring robust agent deployments.
Conclusion
ByteDance's OpenViking sets a new standard for contextual management in AI, offering a scalable, efficient solution that empowers developers to build more intelligent agents. As the project evolves with community contributions, it promises to drive innovation in automation. Explore the GitHub repository today to integrate OpenViking into your AI workflows and unlock its full potential.
